Build A Info About Does IGBT Work On AC Or DC
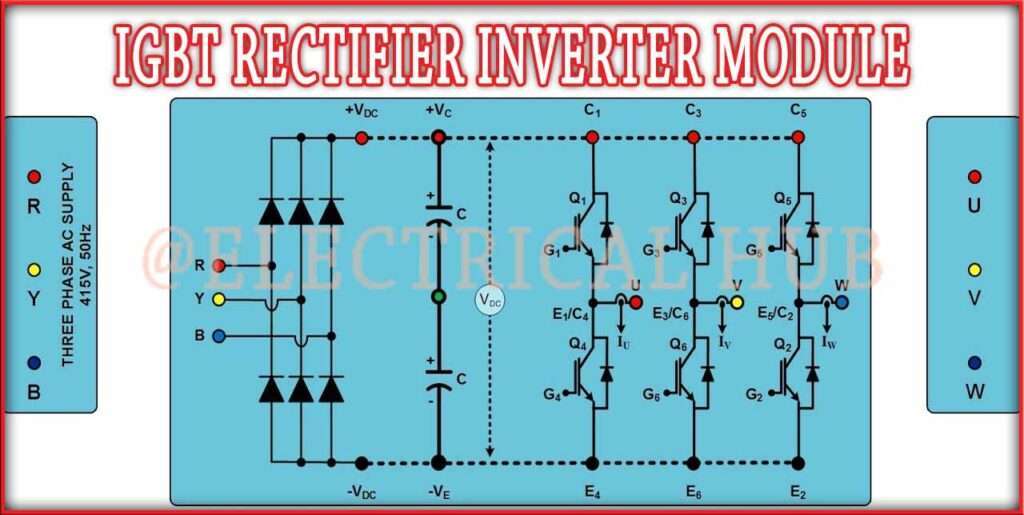
IGBT Rectifier Working, Features And Important Applications
IGBTs
1. Understanding the Basics of IGBTs
Alright, let's dive into the world of IGBTs — Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors. Quite a mouthful, isn't it? These little semiconductor heroes are vital components in power electronics, controlling hefty amounts of electrical energy. Think of them as super-efficient switches that can handle both voltage and current with impressive speed. But here's the question that often pops up: are they AC-friendly, DC devotees, or perhaps a bit of both? Keep reading; we're about to untangle this!
To truly grasp the answer, we need to understand how IGBTs operate. An IGBT essentially combines the best features of two other transistors: the MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) and the BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor). The MOSFET part gives it a high input impedance, meaning it doesn't require much current to control it. The BJT section allows it to handle large currents with relatively low voltage drop. Its the best of both worlds!
Now, imagine an electrical circuit as a highway system. IGBTs act as the traffic controllers, opening and closing lanes to direct the flow of electrons. These controllers are incredibly responsive, switching on and off in microseconds, which makes them perfect for applications requiring precise control of power. They're commonly used in things like variable frequency drives (VFDs), electric vehicles, and even your friendly neighborhood induction cooktop.
Thinking about the "AC or DC" question, it is important to remember that IGBTs are unidirectional devices. This means that they are designed to control current flow in one direction only. This characteristic has significant implications when we consider the types of applications where IGBTs are most useful.
So, Does the IGBT Prefer AC or DC?
2. The IGBT's DC Dominance
The short answer? IGBTs are primarily DC devices. Now, before you start scratching your head, let's clarify why. While you might find them in AC circuits, they don't directly switch AC voltage in the same way a triac or back-to-back SCRs would. The magic lies in how they are used in AC applications.
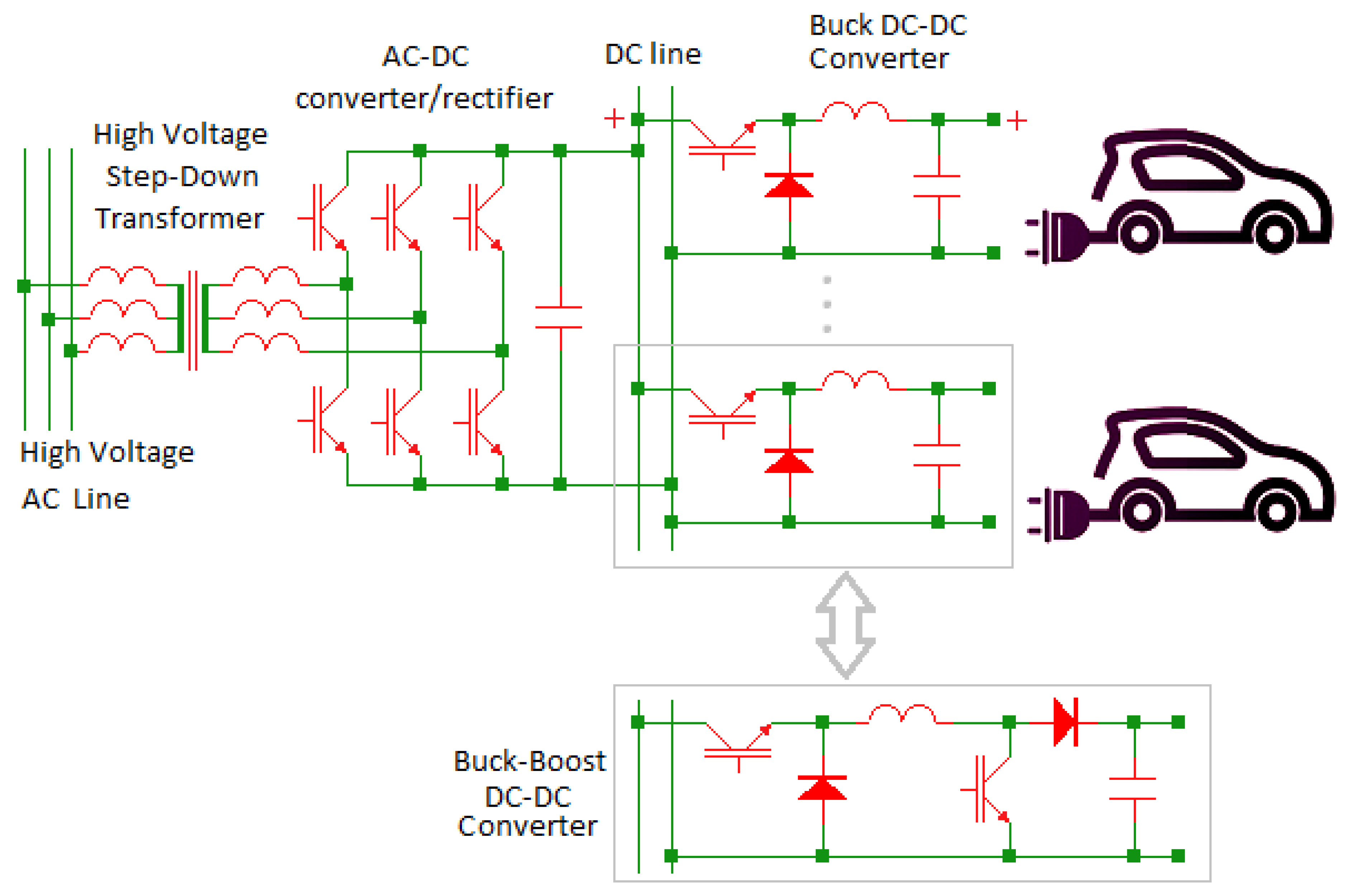
Here's where things get interesting: IGBTs are frequently employed in inverters and rectifiers. These circuits are essential for converting DC power into AC (inverters) and AC power into DC (rectifiers). So, while the IGBT itself is switching DC, it plays a vital role in systems that ultimately handle AC power. Think of it like a translator who speaks only one language fluently but helps people communicate across different languages.
Consider a solar panel system. Solar panels generate DC electricity. To use that electricity in your home, which runs on AC, you need an inverter. Inside that inverter, IGBTs are tirelessly switching the DC voltage to create an alternating current waveform. Without IGBTs, you'd be stuck watching Netflix on a potato battery! (Okay, maybe not, but you get the idea.)
To expand, even if you see an IGBT "handling" AC, what's really happening is sophisticated circuitry is using the IGBT to chop up or create AC waveforms from DC sources. So, it's less about the IGBT being inherently an AC device and more about its clever deployment in AC-related applications. The true power of an IGBT isn't necessarily in AC power, but its ability to handle and control DC power, used within AC systems.

Igbt Transistor Working Principle At Amber Girdlestone Blog
The Role of IGBTs in AC Systems
3. IGBTs as Part of the AC Ecosystem
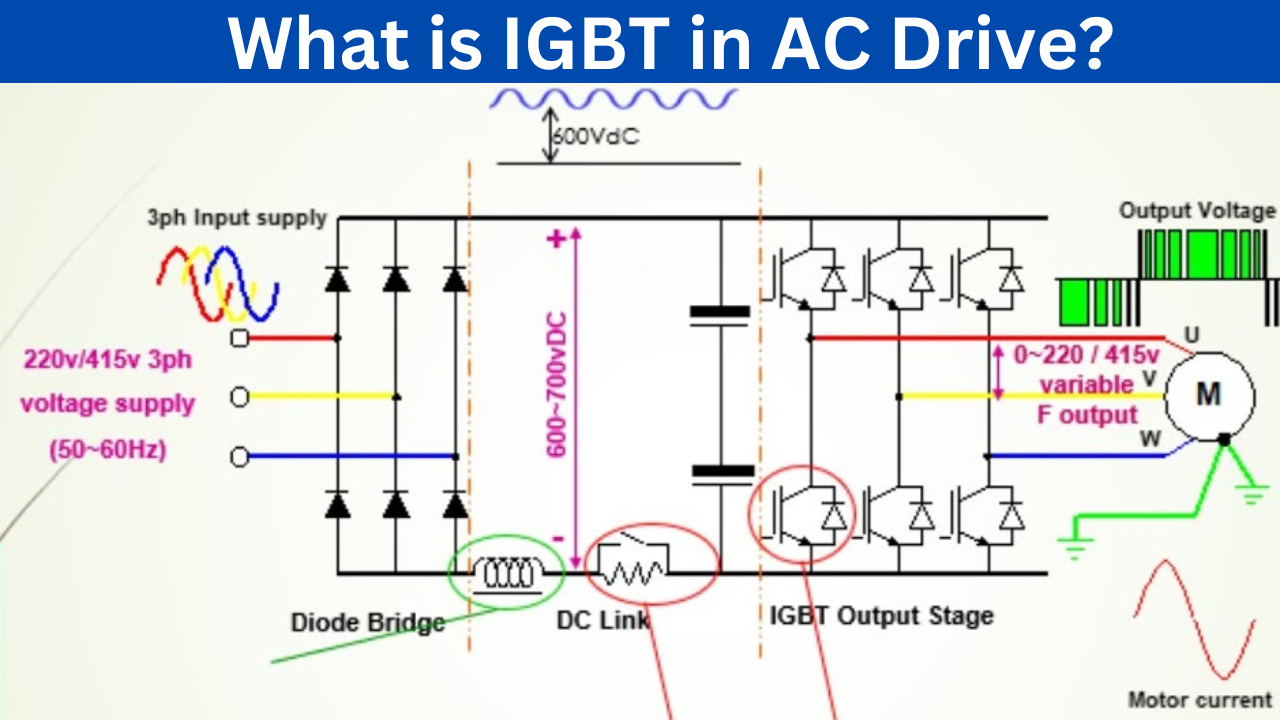
Think of an AC motor drive. These drives control the speed of AC motors by varying the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor. The inverter section of the drive, powered by IGBTs, converts DC power from the power supply into AC power with the desired frequency. The IGBTs are rapidly switching the DC voltage on and off to synthesize the AC waveform. Without these switching superheroes, controlling motors would be a far less efficient — and far less precise — endeavor.
The beauty of using IGBTs in these kinds of applications is their ability to switch quickly and efficiently. This rapid switching allows for the creation of very precise AC waveforms, minimizing harmonic distortion and improving overall system performance. It's like having a sculptor who can carve a perfect statue with incredible speed and accuracy.
Another area where IGBTs shine in AC systems is in UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems. In the event of a power outage, the UPS instantly switches to battery power to keep your critical equipment running. The inverter within the UPS, driven by IGBTs, converts the battery's DC power into AC power, ensuring a seamless transition and preventing your computer from crashing mid-game. That's a true friendship!
Therefore, while IGBTs might not be directly switching AC voltage, their role in creating and controlling AC power in a wide variety of applications is undeniable. Their ability to efficiently and precisely switch DC voltage is what makes them so valuable in the AC world.

Why IGBTs Excel
4. IGBT Benefits and Where They Shine
So, what makes IGBTs so great, anyway? Well, for starters, they boast high efficiency. This means they waste very little energy in the form of heat when they're switching. This is crucial in high-power applications where efficiency directly translates to lower energy bills and reduced cooling requirements. No one likes wasting energy, right?
Another advantage is their fast switching speed. This allows them to create high-frequency AC waveforms with minimal distortion. Faster switching also means smaller and lighter filter components can be used, which is a win-win for space-constrained applications. Think about the advancements in electric vehicles; the smaller and more efficient the components, the better the performance and range!
Beyond the inverter and rectifier applications we've already discussed, IGBTs are also widely used in welding machines, induction heating systems, and even high-voltage DC (HVDC) transmission systems. In each of these applications, the IGBT's ability to efficiently and reliably control high power levels is paramount.
Furthermore, IGBTs are robust devices, capable of withstanding high voltages and currents. This makes them suitable for demanding applications where reliability is critical. Consider the environment within an industrial welding machine — it's a harsh, electrically noisy place. IGBTs are designed to perform reliably under these conditions, ensuring consistent and safe operation.
In Summary
5. Wrapping Up the AC/DC Discussion
So, let's recap. While IGBTs are fundamentally DC devices that control current flow in one direction, they are indispensable in a plethora of AC applications. They serve as the unsung heroes in inverters, rectifiers, motor drives, and UPS systems, efficiently switching DC voltage to create and control AC power. Their high efficiency, fast switching speed, and robustness make them the go-to choice for power electronics engineers worldwide.
Next time you're using an appliance powered by an inverter, or driving an electric car, remember that the humble IGBT is working tirelessly behind the scenes to make it all happen. It's a reminder that even the smallest components can play a huge role in shaping the world around us.
Basically, think of IGBTs as the versatile utility players of the electronics world. They might not be the flashy quarterbacks grabbing all the headlines, but they're the ones consistently delivering solid performance, game after game. And in the world of power electronics, consistency and reliability are the name of the game.
To finalize, remember that while IGBTs work primarily with DC, their impact on AC systems is significant. They are the critical link in enabling the efficient conversion and control of electrical power in a wide range of applications.