Marvelous Tips About Is 460V Always 3 Phase

Decoding the Mystery
1. Untangling the Electrical Web
Okay, let's dive straight into it. You've heard the term "460V," and maybe you've also heard "3-phase power." Are they joined at the hip? Do they waltz together at electrical engineering parties? Well, not always. While the connection is strong, it's not a guaranteed lock.
Think of it like this: a good detective doesn't jump to conclusions. Just because you see someone wearing a trench coat doesn't automatically make them a private investigator, right? Similarly, 460V often indicates 3-phase power in many industrial and commercial settings, but it's not a universal law of physics etched in stone. It's more like a very, very strong suggestion.
So, what makes this connection so strong? Well, 460V is a common voltage level chosen for 3-phase systems because it provides a sweet spot. It allows for efficient power transmission and distribution while keeping the current levels manageable. Higher voltage means lower current for the same power, reducing losses due to resistance in the wires. It's all about efficiency, really.
However, the important takeaway here is that the presence of 460V doesn't automatically tell the whole story. You need to put on your electrical detective hat and investigate further! You need to look at the wiring configuration, the equipment being powered, and maybe even consult the electrical schematics (if you can find them without causing a power outage!).
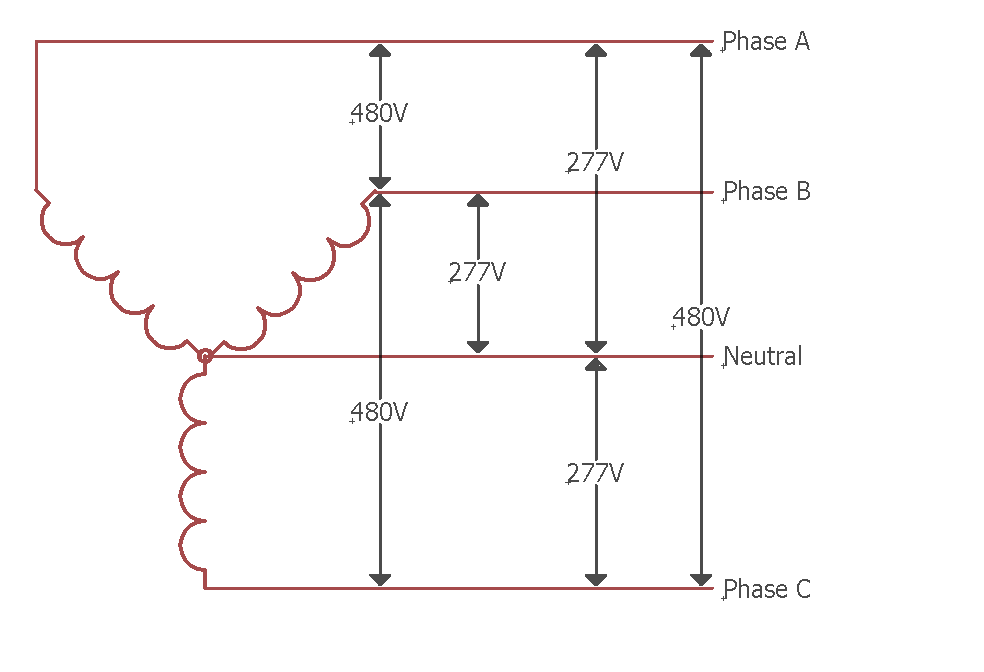
What Is A 3 Phase In Electrical At Catherine Fletcher Blog
Digging Deeper
2. The Power of Three (Phases, That Is)
The primary reason 460V is often associated with 3-phase systems lies in its practical advantages for handling significant electrical loads. Three-phase power, in its simplest form, is like having three separate power lines slightly out of sync with each other. This creates a smoother, more consistent power delivery compared to single-phase, which is like a series of power pulses.
Imagine trying to row a boat with one oar versus three synchronized oars. Which boat is going to move smoother and faster? Three-phase power does the same thing for motors and heavy machinery — it provides a more efficient and balanced power source.
460V, being a common voltage rating for industrial machinery, naturally fits into this 3-phase framework. It's a sweet spot for delivering the power required without excessively high current levels. This makes the wiring easier to manage and reduces energy loss.
Think of industrial settings with massive motors running conveyor belts, HVAC systems, and all sorts of heavy-duty equipment. These applications thrive on the stable and efficient power delivery of 3-phase systems, and 460V is often the voltage of choice.

ATO 40hp 30kW Three Phase VFD, 60A 460V 3 Input
The Exceptions to the Rule
3. Unmasking the Electrical Imposters
Now for the fun part — the exceptions! Just when you thought you had it all figured out, the electrical world throws you a curveball. While 460V is predominantly used for 3-phase systems, it can sometimes be found in single-phase applications, though it's significantly less common. These scenarios are often related to specific equipment requirements or legacy systems.
One potential reason you might encounter 460V single-phase is in situations where a step-up transformer is used. For example, a lower voltage single-phase supply could be stepped up to 460V for a specific piece of equipment. This is typically done to accommodate the equipment's design requirements or to minimize voltage drop over a long distance.
Another possibility is within specialized equipment itself. Internally, a device might use a 460V single-phase circuit for a particular function, even if the main power input is something else entirely. It's all about what's happening behind the scenes within that electrical box!
Always remember to verify the wiring and configuration. Don't rely on assumptions. Thinking you have 3-phase when it's actually single-phase (or vice versa) can lead to equipment malfunction and potentially dangerous situations.

380...460 V, 3 Phases, Normal Duty, ATV600, 1.5kw/2HP, VFD, Inverter
Safety First
4. Becoming an Electrical Safety Guru
Before you go poking around with wires and multimeters, let's talk safety. Electrical work can be dangerous, so always prioritize safety. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, please, please call a qualified electrician. Seriously.
The best way to determine whether a 460V system is 3-phase or single-phase is to use a multimeter. A multimeter can measure the voltage between different points in the circuit. In a 3-phase system, you should be able to measure the voltage between each of the three phases, and also the voltage from each phase to neutral (if there is one).
Another good practice is to check the equipment's nameplate. The nameplate should clearly indicate the voltage and phase requirements. It's usually a small metal plate attached to the device, listing its electrical specifications.
Finally, examine the wiring. Three-phase systems typically have three hot wires (plus a neutral and ground), while single-phase systems usually have just one hot wire (plus a neutral and ground). But again, don't just rely on the number of wires — verify with a multimeter!

Multi Function VFD Frequency Inverter 3 Phase 460V Air Cooling Metal Case
The Bottom Line
5. Wrapping Things Up (and Avoiding Electrical Shock)
So, "Is 460V always 3-phase?" The short answer is no, but it's highly likely, especially in industrial settings. The key takeaway is this: don't make assumptions. Always verify the voltage and phase using appropriate tools and techniques. Think of it like a doctor diagnosing a patient — you wouldn't prescribe medication based on a hunch, would you?
Context is crucial. Knowing the type of equipment being powered, the setting (industrial vs. residential), and the electrical codes in your area can all provide clues. But ultimately, accurate measurements are the most reliable way to determine the actual configuration of the system.
Electrical systems can be complex. If you're unsure about anything, don't hesitate to consult a qualified electrician. They have the training and experience to safely and accurately diagnose electrical issues. Remember, a little bit of caution can go a long way in preventing accidents and ensuring that your electrical systems are operating safely and efficiently.
Consider this the next time you see that ominous "460V" label: approach with caution, verify with measurements, and remember that the electrical world is full of surprises! Stay safe, stay informed, and maybe invest in a good multimeter.

Motor, Power Pack, 7.5HP, 1770RPM, 213TYZ Frame, TEFC Enclosure, 3
FAQs
6. Quick Answers to Common Queries
Here are some frequently asked questions about 460V and 3-phase power:
Q: What happens if I try to run a 3-phase motor on single-phase power?
A: Bad things! A 3-phase motor needs all three phases to operate correctly. If you try to run it on single-phase power, it likely won't start, and if it does start, it will run very inefficiently and may overheat and be damaged. Don't do it!
Q: Can I convert single-phase power to 3-phase power?
A: Yes, you can! There are devices called rotary phase converters or variable frequency drives (VFDs) that can convert single-phase power into 3-phase power. These are often used in situations where 3-phase power is not readily available.
Q: Is 460V dangerous?
A: Absolutely! Any voltage above 50V is considered potentially dangerous. 460V can cause severe electrical shock, burns, and even death. Always take appropriate safety precautions when working with electricity. Turn off the power before working on any electrical equipment, use insulated tools, and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).